Singaporeans are a competitive bunch. One of the must-know Singlish words for those living in the city-state is kiasu. The Chinese Hokkien term roughly means a fear of missing or losing out and often refers to someone trying to get ahead of others. “Fomo on steroids” is how one Singaporean friend describes it.
One of the best places to see this in action is the queues at lunchtime around stalls of the city-state’s favourite hawker food markets. Another area to observe the kiasu mentality in the Asian financial centre is in business, such as foreign investment.
Singapore made a surprise announcement last month that it would free up more power for data centre expansion. The move came as the chief executives of Nvidia, Google, Microsoft and others have been swinging by neighbouring Malaysia — and other countries in south-east Asia — in recent months pledging billions in data centre investment.
In Malaysia alone, the tech groups — three of the top four biggest companies by market capitalisation globally — have committed $8.5bn in new data centre, cloud and artificial intelligence investment in the past six months. Which is why more than one Malaysian government official joked that Singapore’s decision to court more data centres was a “typical Singapore kiasu response” to its neighbour’s progress.
Of course there is some competition between Singapore and its neighbours, especially Malaysia from which it gained independence in 1965. But it is overly simplistic to dismiss Singapore’s move as kiasu-ness — even if there is an element of that at play. The city-state is already hyper connected and one of the biggest data centre markets in Asia — a trend that accelerated as Hong Kong became a less favoured destination for data centres and undersea cables. It is one of the top submarine cable hubs globally, with connections to 25 active subsea cables and more to come. None of that will change soon.
The decision to increase data centre capacity last month was a surprise to many because the government imposed a more than three-year moratorium on new data centres between 2019 and 2022. The proliferation of the energy-guzzling facilities had been consuming a substantial amount of Singapore’s resources. That ban helped push data centre companies into nearby Johor, the Malaysian state just across the causeway, and to a certain extent Batam, a close-by Indonesian island.
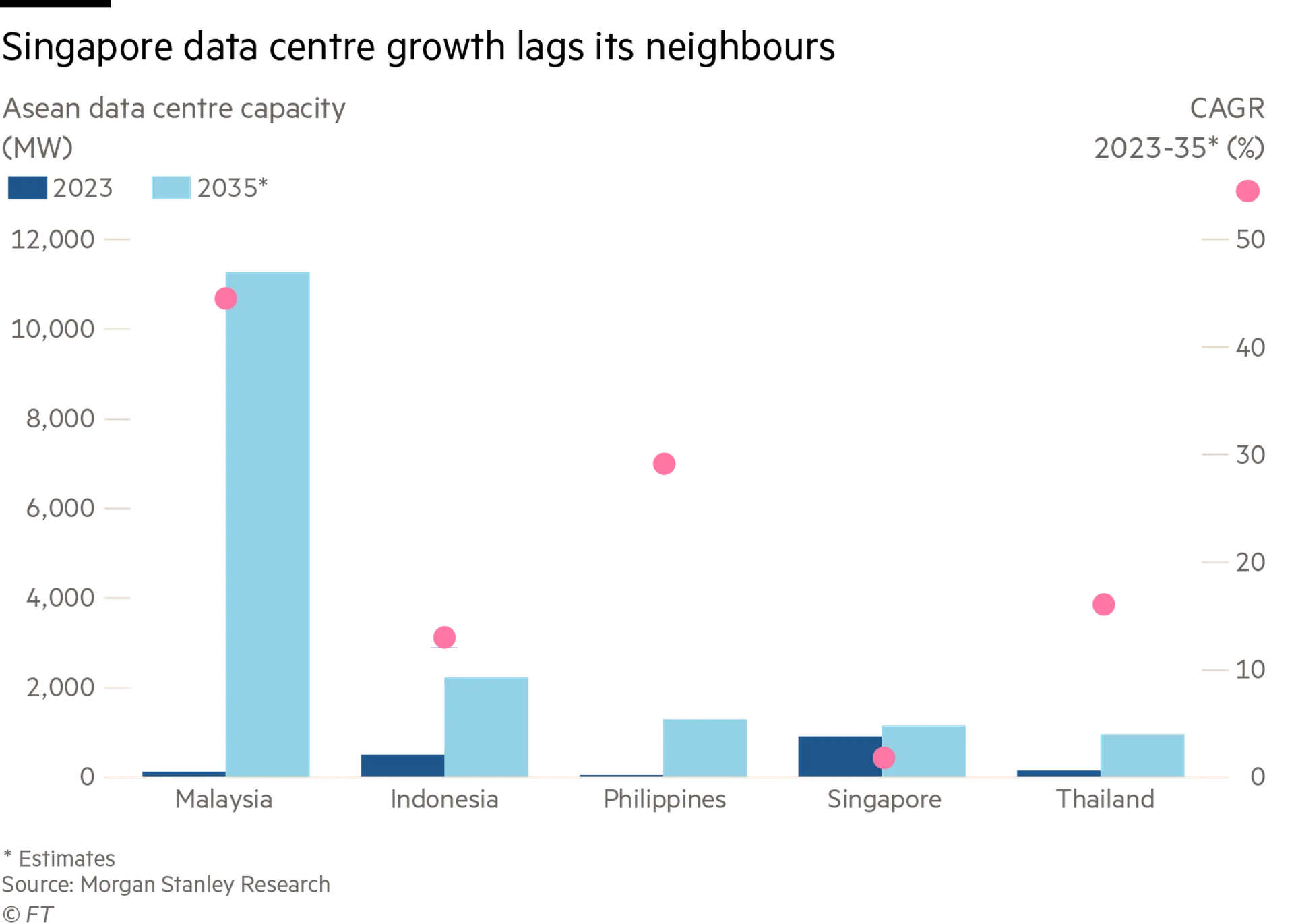
The conundrum Singapore faces now — like many other countries — is that it grossly underestimated how demand for AI is going to expand the global market for data centres in coming years. The city-state has made little secret of the fact that it wants to be the AI hub for south-east Asia, if not the top in Asia.
That’s because being such a hub brings other economic benefits. For example, as part of Nvidia’s data centre investment in Malaysia, the company will partner with local conglomerate YTL Power to develop the country’s fastest supercomputers using Nvidia’s AI chips. Microsoft last month unveiled landmark AI infrastructure investments in Indonesia and Thailand.
Singapore realises it cannot ultimately compete with its neighbours for land and power. The key is how to complement it. The reason Johor is popular with global tech giants from ByteDance to Nvidia and Microsoft is because it is just a few kilometres away from hyperconnected Singapore.
“Both Johor and Singapore can benefit from the data centre boom. They complement each other,” says Rangnath Salgame, chair and chief executive of Princeton Digital Group, an Asian data centre company based in Singapore but expanding in Johor. It is a “symbiotic relationship”, he adds.
And as more and more companies diversify supply chains away from China that puts Singapore in pole position. One way it can benefit is by promoting a Singapore + one strategy, whereby companies establish a headquarters in the country to leverage its international business environment, free trade agreements and access to professional talent, but then have their manufacturing — or data centre — facilities in places such as Johor.
This is already a long-term trend. Singapore was the top recipient of inward foreign direct investment flows in south-east Asia between 2013 and 2022, according to the latest data published by the bloc. In 2022, Singapore attracted $141bn of FDI, accounting for more than half of the region’s total. So should Singapore really be kiasu?